
If A is non-singular, thanĭoes not exist (because A is not square or A is singular): The rank of a non-singular matrix equals the number of rows (or columns).A non-singular matrix has a non-zero determinant. Singular matrixĪ matrix is said to be singular if its inverse does not exist, otherwise non-singular.

The trace of a square matrixĮxists if and only if A is non-singular. The rank of a matrix is the number of linearly independent rows (or columns). If the dimension of the matrix A is r x c, the dimension of its transpose is c x r.Ī square matrix is said to be orthonormal if The transpose of a matrix is shown as AT and is simply obtained by writing the rows of A one by one as columns of AT. The identity matrix has the following property: The matrix whose elements other than the diagonal elements, are zero, is called as a diagonal matrix as:Īn identity matrix is a diagonal matrix whose diagonal elements is one and represented by I. The diagonal elements of this matrix are a11, a22, a33.ann. The general form of a square matrix can be written as If n is a positive integer and A is a square matrix than the nthpower of A is calculated by multiplying itself n times asĪ matrix, whose number of rows and columns are equal, is called a square matrix. Matrix product is associative, distributive over addition and subtraction, but not commutative: The elements of matrix C, which is the product of matrix The multiplication of a matrix with a scalar value k is obtained by multiplying every element of the matrix with the scalar as:
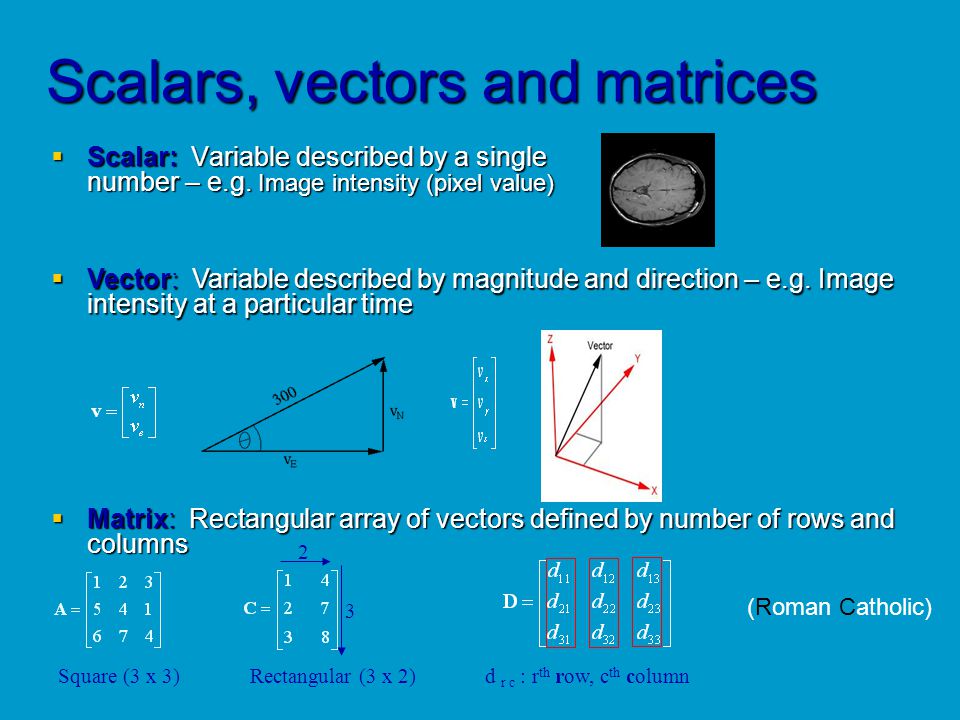
The difference of two matrices is defined similarly as: In order to add two matrices, their dimensions should also be equal and is defined as:Īddition of matrices has associative and commutative properties: Matrix Addition, Subtraction, Multiplication A vector with one row is referred to as row vector, and a vector with one column is referred to as column vector. Represents n-dimensional space, and thus, A represents a point in this space. Which are composed of n real elements such that Vectors are usually shown as a column matrix as: If all the members of a matrix are numbers, the matrix is refered as a constant matrix.Ī matrix with one row or column is called as vector. If at least one element of a matrix is a complex number or a complex-valued function, the matrix is called complex valued. The dimension of a matrix with r rows and c columns is called r by c, and usually written as r x c.Ī matrix is called real-valued, if all the elements of the matrix are real valued numbers or functions. Matrices are shown with bold capital letters. Chapter 2 Matrix Theory and Applications with MATLABĪ matrix is a rectangular array, which is arranged as horizontal row and vertical column elements and is shown in brackets.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
